2024. 2. 20. 23:46ㆍJAVA
TreeSet
TreeSet은 범위 탐색, 정렬에 특화 돼 있다.
이진 탐색 트리(binary search tree)로 구현 돼 있다.
이진 트리는 모든 노드가 최대 2개의 하위 노드를 갖는다.
각 요소(Node)가 나무(tree) 형태로 연결된다.(LinkedList 의 변형으로 생각하면 편함)

class TreeNode{
TreeNode left;
Object element;
TreeNode right;
}
링크드 리스트랑 비슷하다
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
}LinkedList 의 Node는 이전, 이후 노드 정보를 갖지만,
TreeSet 의 Node 는 Left, Rgiht 로 하위 노드를 갖는다. (하위 Node에서 상위 Node 정보를 모른다느느 말이기도 하다)
이진 탐색 트리(binary search tree)
'이진 탐색 트리'는 '이진 트리'의 한 종류로 값을 아래와 같이 담는다.
부모보다 작은 값 -> 왼쪽
부모보다 큰 값 -> 오른쪽
('이진 트리' 는 값 크기에 따라 왼쪽 오른쪽 분간 없이 하위 Node 최대 2개)
이진 트리 구조는 데이터가 많아질수록 추가, 삭제에 시간이 오래 걸림(비교 횟수가 증가하기 때문에)
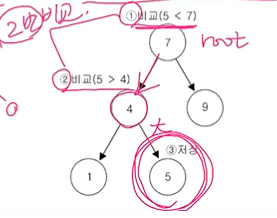
TreeSet 데이터 저장 과정
boolean add(Obejct o)
앞서 학습한 HashSet 에 객체를 저장할 때 저장할 객체에서 equals() 와 hashCode()를 호출해 객체를 비교 한다고 했음.
TreeSet에서는 compare()를 호출하여 비교함.

TreeSet 주요 메서드
TreeSet() - 기본 생성자
TreeSet(Collection c) - 주어진 컬렉션을 저장하는 TreeSet 생성
TreeSet(Comparator comp) - 주어진 정렬기준으로 정렬하는 TreeSet 생성(Comparator 는 비교 기준 제공)
* Comparator로 정렬기준을 넣지 않는 경우, 저장하는 객체가 가진 Comporatable(기본 정렬 기준)을 사용함.
Obejct first() - 정렬된 순서에서 첫 번째 객체를 반환함.
Obejct last() - 정렬된 순서에서 마지막 객체를 반환함.
Object ceiling(Obejct o) - 지정된 객체와 같은 객체 반환. 없으면 큰 값을 가진 객체 중 제일 가까운 객체 반환. 없으면 null
Object floor(Object o) - 지정된 객체와 같은 객체 반환. 없으면 작은 값을 가진 객체 중 가장 가까운 값의 객체 반환. 없으면 null
Object higher(Obejct o) - 지정된 객체보다 큰 값을 가진 객체 중 가장 가까운 값의 객체를 반환. 없으면 null
Object lower(Obejct o) - higher 반대
SortedSet subSet(Object fromElement, Object toElement) - 범위 검색(fromElement와 toElement 사이의 결과를 반환. 끝 범위 미포함
SortedSet headSet(Obejct toElement) - 지정된 객체보다 작은 값의 객체들을 반환함.
SortedSet tailSet(Obejct fromElement) - 지정된 객체보다 큰 값의 객체들을 반환함.
예제1
- TreeSet 과 HashSet 비교
public class TreeSet_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Set set = new TreeSet(); // binary search tree 이진 탐색 트리. 정렬o
Set set = new HashSet(); // 정렬 안 됨. binary tree 이진 트리. 정렬x
for (int i = 0; set.size() <6 ; i++) {
int num = (int)(Math.random()*45) +1;
set.add(num); // set.add(new Integer(num)); 과 같음. 오토박싱
}
System.out.println(set);
}
}
예제2
Comparator도 Comporatable 도 없는 객체를 set에 넣으려고 하면?
public class TreeSet_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new TreeSet(); // binary search tree 이진 탐색 트리. 정렬o
// 런타임 오류. ClassCastException
// set.add(new Test());
}
}
class Test{
// Comparable 이 없는 일반 class
}
에러 내용
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassCastException: class collection_.Test cannot be cast to class java.lang.Comparable (collection_.Test is in unnamed module of loader 'app'; java.lang.Comparable is in module java.base of loader 'bootstrap')
Test 클래스는 Comparable 로 컨버트될 수 없다.
왜 Comparable 이 필요한가?
위의 예제에서 Set의 구현체는 TreeSet 이다.
TreeSet은 이진 탐색 트리 구조이다.
작은 값은 왼쪽, 큰 값은 오른쪽으로 정해놓고 객체를 저장하는 구조이므로, 비교가 반드시 발생해야 한다.
현재 Test 클래스에는 비교를 위한 Comopratable 를 상속하지 않으므로, 비교가 불가능하다.
-> TreeSet은 정렬을 위해 비교가 필요한데 비교(정렬) 기준이 없어서 오류가 발생함.
요약
회피 방법1
비교가 따로 필요없는 HashSet 으로 구현체를 바꾸면 오류 발생 안 함.
회피 방법2
Comparator 혹은 Comparatable을(혹은 구현체를) TreeSet의 생성자에 넣어주면 됨.
Set set = new TreeSet(new TestComp());
class TestComp implements Comparator {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return -1;
}
}
예제3
subSet 따라 쳐보
public class TreeSet_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet set = new TreeSet();
String from = "b";
String to = "d";
set.add("abc");
set.add("car");
set.add("dance");
set.add("element");
set.add("floor");
set.add("Disco");
set.add("Eminem");
System.out.println(set);
System.out.println("range search : from " + from + " to " + to);
System.out.println("result1 : " + set.subSet(from, to));
System.out.println("result2 : " + set.subSet(from, to + "zzz"));
}
}'JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Generics_제한 (0) | 2024.03.21 |
|---|---|
| Optional<T> (0) | 2024.02.23 |
| 컬렉션_HashSet_2 (0) | 2024.02.20 |
| 컬렉션_HashSet(1) (0) | 2024.02.19 |
| 컬렉션_Iterator 과 Map (0) | 2024.02.17 |